Fluorite Beneficiation and Processing Plant
HZE will conduct feasibility studies based on the condition of the raw ore, the metallurgical test report, the customer's mineral reserves and investment scale, and the conditions for building the plant, then propose a complete set of solutions for the plant which includes engineering design, equipment manufacturing and supply, logistics, installation, commissioning, training, trial production and so on to ensure advanced technology, perfect processing, efficient plant construction, reduced investment, environmental protection and maximum benefits.
Uses of Fluorite
Fluorite has a wide variety of uses. The primary uses are in the metallurgical, ceramics, and chemical industries; however, optical, lapidary, and other uses are also important.
Fluorspar, the name used for fluorite when it is sold as the concentrate after processing has the following three different grades.
Acid Grade Fluorspar
Acid grade fluorspar is a high-purity material used to produce hydrofluoric acid (HF). It contains over 97% CaF2. The hydrofluoric acid is then used to manufacture a variety of products.
Ceramic Grade Fluorspar
Ceramic grade fluorspar contains between 85% and 96% CaF2. Much of this material is used in the manufacture of specialty glass, ceramics, and enamelware. Fluorspar is used to make glazes and surface treatments that produce hard glossy surfaces, opalescent surfaces, and a number of other appearances that make consumer glass objects more attractive or more durable.
Metallurgical Grade Fluorspar
Metallurgical grade fluorspar contains between 60 and 85% CaF2. Much of this material is used in the production of iron, steel, and other metals. Fluorspar can serve as a flux that removes impurities such as sulfur and phosphorous from molten metal and improves the fluidity of slag.
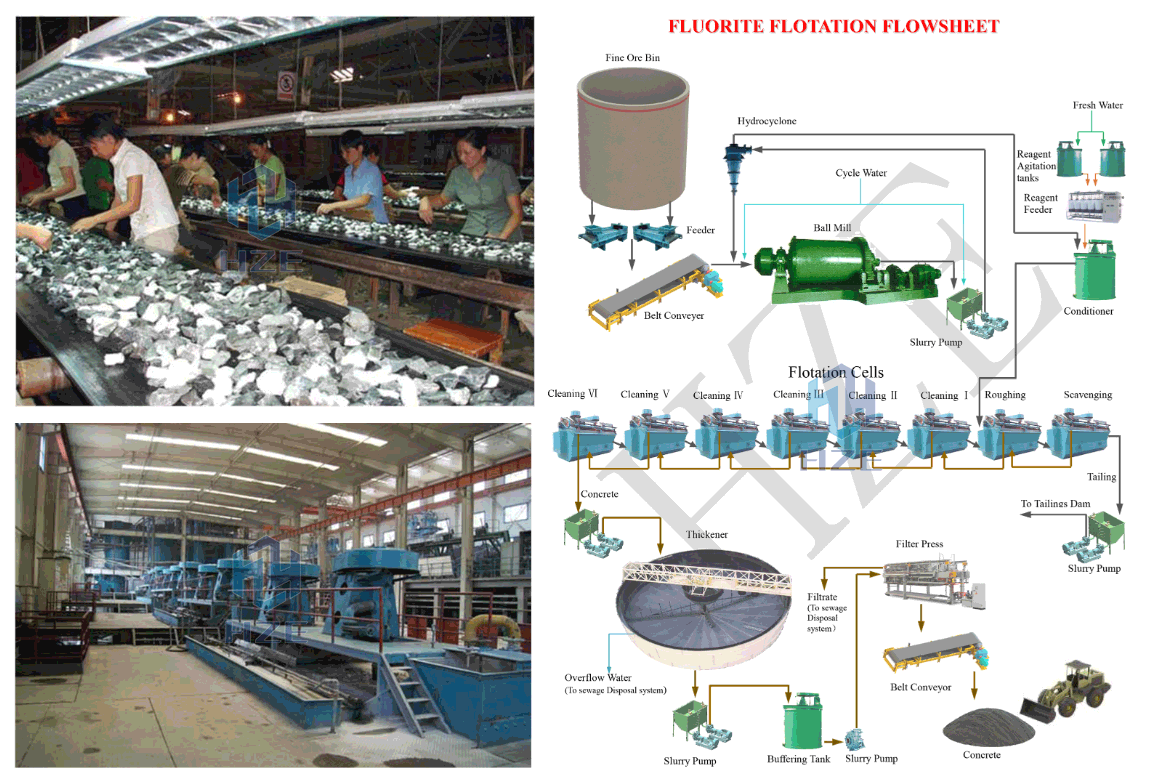
Mineral processing
The common processing methods include manual sorting, gravity separation and flotation. The good products can be obtained after at least 6 stages of cleaners of flotation usually.
The concentrate after flotation is generally dewatered by thickening and filtration, and then packaged and sold to the smelting plant.
The tailings after flotation are pumped to the tailings impoundment or the tailings are dewatered for dry stacking.