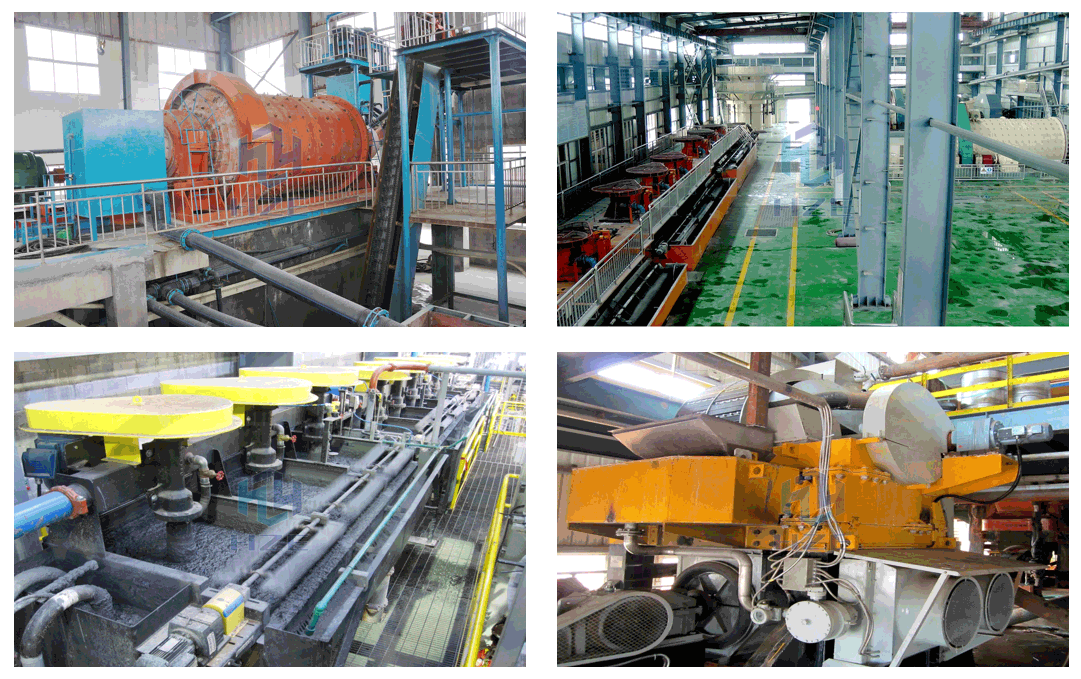
Feldspar Beneficiation and Processing Plant
HZE will conduct feasibility studies based on the condition of the raw ore, the metallurgical test report, the customer's mineral reserves and investment scale, and the conditions for building the plant, then propose a complete set of solutions for the plant which includes engineering design, equipment manufacturing and supply, logistics, installation, commissioning, training, trial production and so on to ensure advanced technology, perfect processing, efficient plant construction, reduced investment, environmental protection and maximum benefits.
Feldspar ore is the main source of feldspar mineral concentrate or purified feldspar used in the manufacture of various grades of glass and ceramics including high-end ceramics and electronic-grade glass fibers. The glass and ceramic industries, in particular, are major consumers of feldspar, accounting for 95% of total consumption.
In recent times, the increasing rate of depletion of high-grade feldspar ores has resulted in lower-grade ores becoming the primary source of feldspar. This has placed added pressure on producers to further optimize existing feldspar processing methods like flotation to more efficiently produce higher grades of feldspar for the specialty glass, ceramics and electronics markets.
When manufacturing high-grade, colorless glass it is important to have very low levels of iron oxide in the feldspar. Avoiding the presence of iron in the batch composition of glass is preferred because iron, even in very small quantities, can color glass and cause production problems. When manufacturing white wares, although higher percentages of iron content in feldspar may be permissible, the levels of iron allowed are still very low.
Flotation concentration is the most widely used and preferred method to purify raw feldspar ores in addition to the desliming, magnetic and gravity methods. So the reasonable reagent sorts and dosage are very important.
The concentrate after flotation is generally dewatered by thickening and filtration, and then packaged and sold to the smelting plant.
The tailings after flotation are pumped to the tailings impoundment or the tailings are dewatered for dry stacking.